Managing multiple user logins in WordPress can significantly benefit any website. Proper user management allows administrators to distribute tasks, maintain security, and foster collaboration.
This guide helps WordPress site owners, administrators, and developers understand key aspects of multi-user management, including user roles, account creation, permission settings, and more.
The Importance of Multiple User Accounts
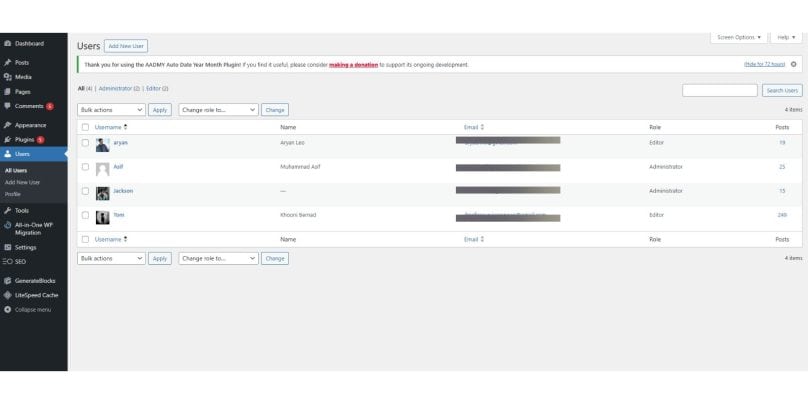
Multiple user accounts allow team collaboration and clear role division, ensuring each user has the specific access needed for their tasks without compromising security. For instance, content creators can publish and edit posts, while only administrators have full control over site settings.
Assigning individual accounts also enhances security by reducing the risks of shared credentials. For more on online security and risk management, check out these techniques to avoid common security pitfalls.
Creating New User Accounts in WordPress
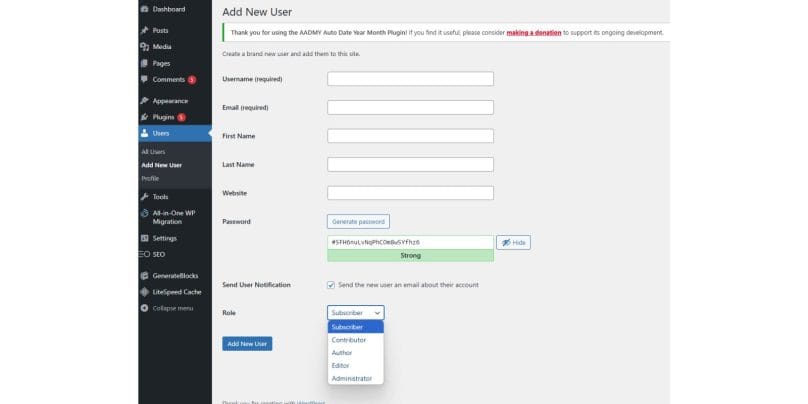
Adding a new user in WordPress is straightforward:
- Log in to your WordPress admin dashboard.
- Click “Users” in the left menu, then select “Add New.“
- Fill in the username, email, and other fields, assigning a unique username to each user.
- Generate a strong password for the new user or let them set one upon login.
- Click “Add New User” to send the login details via email.
Following these steps allows you to quickly add users and assign their roles. To secure and streamline this process further, consider using plugins from the Best Free WordPress Migration Plugins to help manage user transitions smoothly.
Assigning User Roles and Permissions
WordPress provides several user roles with unique permissions:
- Administrator: Full control over the website, including user, settings, plugin, and theme management. Reserved for trusted users.
- Editor: Manages all site content, including posts by others. Typically suited for content managers.
- Author: Can write, edit, and publish their posts but lacks access to others’ content or site settings.
- Contributor: Can write and edit their drafts but cannot publish them; editors or administrators must review their work.
- Subscriber: Has minimal access, usually limited to viewing content and managing their profile. Suitable for subscription-based sites.
Assigning appropriate roles ensures each user has the access necessary for their responsibilities. For more on defining and optimizing user responsibilities, read our guide on Best Notification Bar Plugins.
Managing User Access and Permissions
Managing access levels is crucial for site security. To adjust user roles:
- Go to “Users” in the dashboard.
- Select the user and change their role as needed.
For advanced customization, use plugins like User Role Editor or Members to tailor roles and permissions. Additionally, monitoring user activity with plugins like Simple History or Activity Log helps track changes and prevent unauthorized modifications. You might also consider using insights from Most Frustrating WordPress Errors & How to Fix Them to avoid common access issues.
Handling User Conflicts and Issues
Sometimes, users may face issues logging in or accessing accounts. Here are solutions for common problems:
- Login Problems: Verify the correct username and password. If needed, reset passwords via the “Users” section.
- Inactive or Unused Accounts: Deactivate or delete inactive accounts for security. Transfer any associated content to another user before deletion.
Addressing these issues promptly ensures your site remains secure and efficient. For additional tips, refer to our article on Best WordPress Caching Plugins for optimized site performance during user transitions.
Best Practices for User Management in WordPress
Effective user management involves more than adding roles. Implement these best practices to keep your site secure and user-friendly:
- Ensure Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Encourage strong passwords and consider enabling two-factor authentication for extra security.
- Regularly Review Access: Periodically review user roles and permissions, removing or deactivating users who no longer need access.
- Streamline Onboarding: Ensure new users understand their roles and permissions. An onboarding guide can help large teams start efficiently.
Plugins like WP User Manager or User Role Editor simplify user management, offering greater control and flexibility over permissions. For a deep dive into plugins that streamline your workflow, explore our list of Top WordPress Plugins You Must Have.
Managing Developer Access After Project Completion
When a developer completes a project, ensure their access aligns with ongoing needs:
- Transition from Development to Live: Confirm the site is functional and remove test content or tools if needed.
- Adjust Roles: If the developer had an administrator role, change or remove their access if no longer required.
- Document and Handover: Make sure documentation is available for plugins and configurations. This is valuable for future team members managing the site.
To make this transition seamless, check out 5 Free WordPress Migration Plugins.
Conclusion
Effective multi-user management in WordPress promotes smooth operation, security, and teamwork. By following these steps—creating accounts, assigning roles, monitoring activity, and reviewing permissions regularly—you can maintain a secure, organized site. Implementing best practices further ensures a safe and efficient WordPress experience.
For further reading on keeping your website secure, make sure you regularly check user permissions and integrate necessary security plugins.