During the last decade, there has been a lot of debate on the topic of search engine algorithms and algorithms in general. For a while, in the beginning, nobody cared that much about Google’s feed.
The main focus was on making the #internet function and spreading it to as many users as possible.
First was the period of enjoying the newfound technologies and the opportunities they were offering. Also, daydreaming about the opportunities everybody thought it will offer.
But, as more and more users got on to the internet and started using Google regularly, some holes in the system began to be noticed.
Google’s Ranking Criteria and Algorithm Updates

At first, Google’s interventions were rare. The first update to Google’s algorithm was in 2003.
On November 16, 2003, Google introduced an update we today call “the Florida update”. It was aimed at websites that use tactics like keyword stuffing and multiple sites under the same brand.
Back then, there were a lot of spammy tactics you could use to climb to the top of the search engine results. And just before the holiday season, Google put their foot down and wiped out all websites using these less than valiant tactics.
This also served as sort of a warning that Google was on to these kinds of profit grabbing behavior.
From the “Florida update” in 2003 to 2011 there has been a total of five updates regarding Google’s search algorithm.
Since the beginning of 2011, Google has upped its game drastically regarding these updates. Now, almost once a month Google reviews their algorithm and updates it in many different ways.
The aim of Google’s ranking system is to sort through billions of pages on the internet and offer you the most relevant ones for your search. And to be effective, it has to put up some ground rules that dictate what a website must do to even enter the selection for ranking.
This means that there are some websites that don’t even meet Google’s ranking criteria and cannot be found with Google. And sometimes, website owners deliberately choose not to be found by Google. This is what is known as the “Deep web” or the “Dark web”.
For those that pass the threshold, there are certain parameters Google judges them on. It all depends on your search.
Google will rank pages depending on the words in your query, relevance, usability of pages, the expertise of sources, and your location and settings. Also, depending on what kind of topic you are searching for, the results will be different.
For example, for news queries Google will prioritize the freshest content. While for dictionary searches, content won’t be prioritized based on the time it got posted.
The discussion on what kind of content helps you get on Google’s good side has been going on for a while.
Google also made a guide for creating content called “Webmaster guidelines” you can check out here.
It is mostly about avoiding certain kinds of behavior Google deems as “sneaky” or dishonest.
Google Query and Google Discover
Google places a lot of importance on your query. It is the first line of action that Google takes. No matter how good or important your content is, it doesn’t really mean much unless it’s connected to the query.
Google has a developed system for query analysis that aims to fundamentally understand the motivation of the search. Synonyms, misspell or broadness of the search are all taken into consideration by Google’s system that has been developing for the last 20 years. The work has shown to be positive as we can see the results.
Working on analyzing search queries has brought a lot of new knowledge and experience to Google’s team, and this in turn influenced the development of the Google feed, launched in 2017.
The aim of Google feed is to surface content relevant to your queries without searching for it. Just like Facebook’s feed, Google aimed to anticipate content you would be interested in researching.
The feed has developed into a separate app called “Google Discover”.
The name “Google Discover” is aimed to match the mission of the app: to help users in the process of finding answers, and lead them to discover new and hopefully unexpected but relevant content.
How does this work? Well, Google Discover functions on the principle of “topics”.
Now, topics are not a new thing. Topics have been around on Youtube for a while, and you can even say that hashtags are indeed kind of a “topic”.
Google Discover organizes your queries into topics and offers up content that might be related to your previous searches.
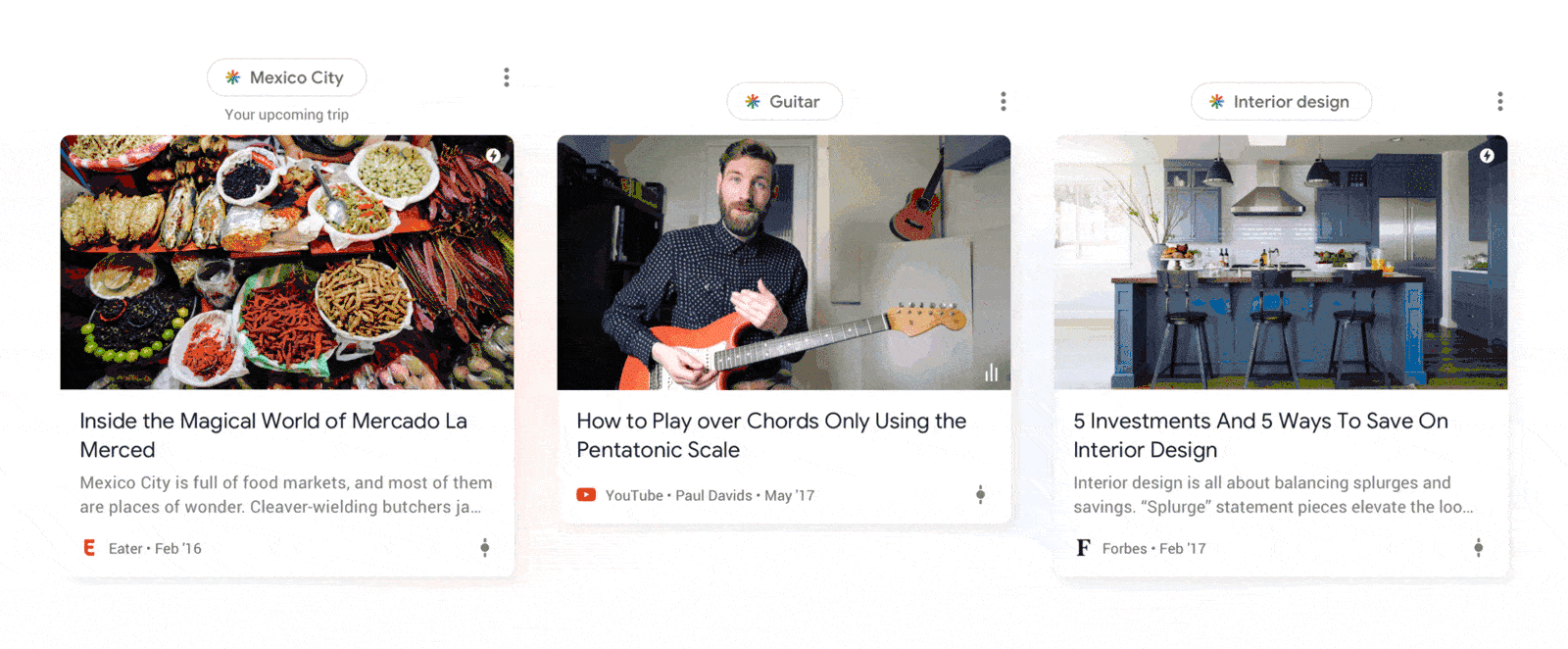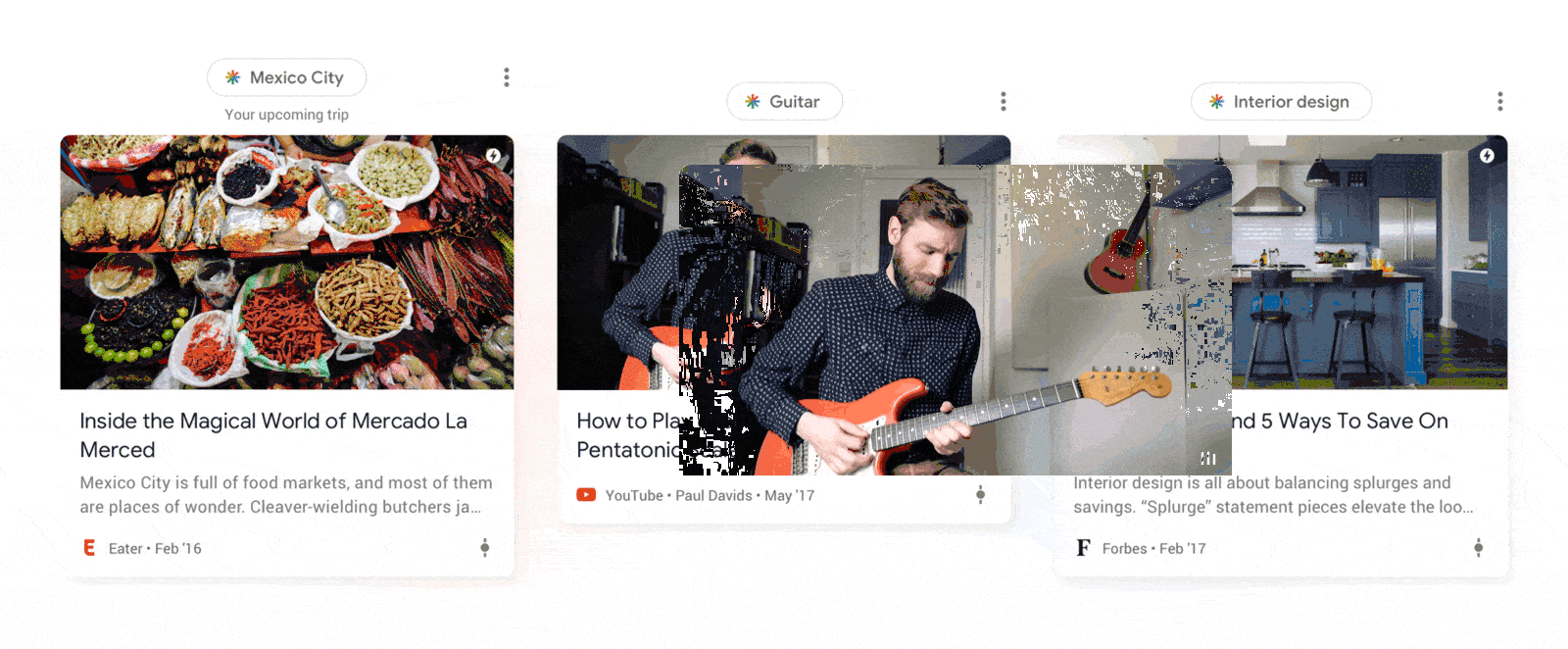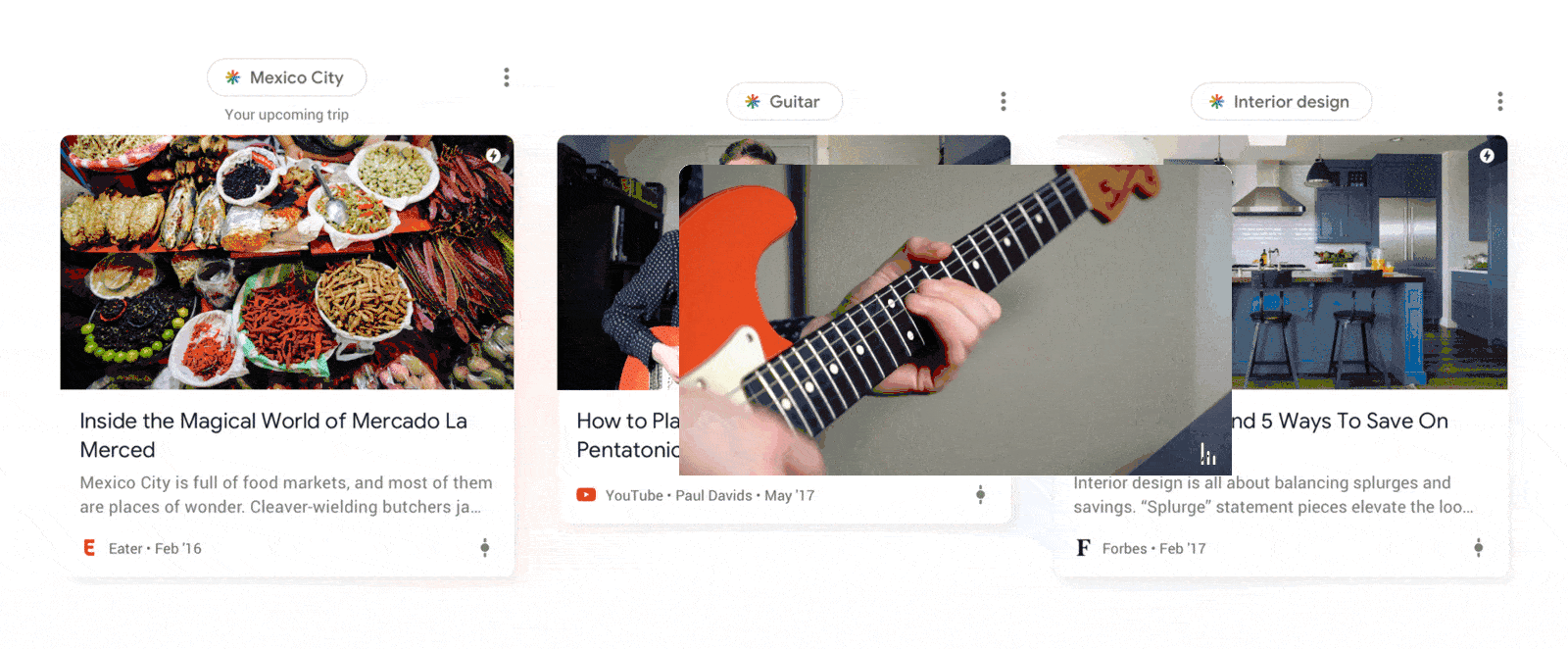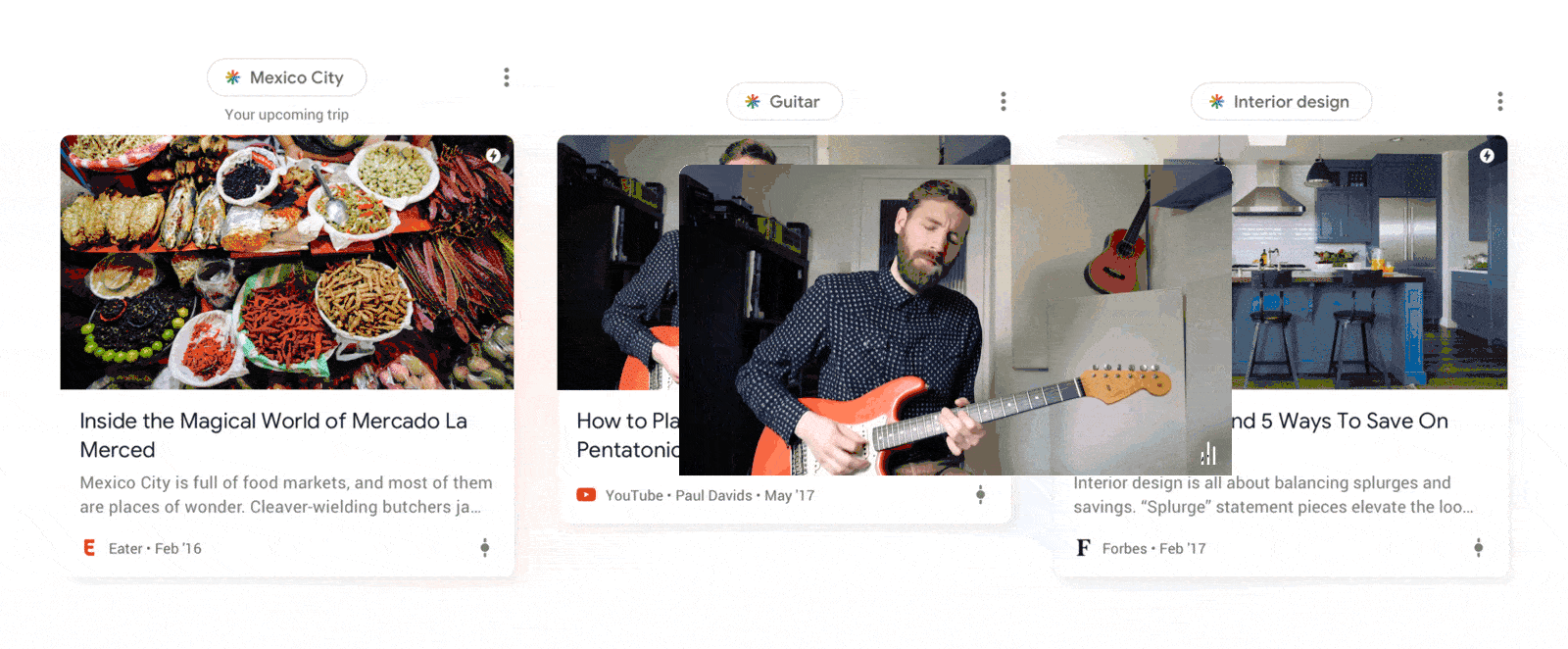
Above every snippet of content that appears on the Google Discover feed, a topic box with the Discover logo and the name of the topic will appear.
This idea of a related content feed came up as Google was noticing that not all searches are short-term.
Remember the last time you needed to write a paper, or plan a trip. Surely you did not find all your answers with just one search. Some searches tend to be longer journeys, and Google’s aim was to accompany you on them and help as much as they can.
With Google Discover, Google aims to surface the content at the right time. Google can predict your level of expertise on a topic and help you develop further. Of course, this is not a one-sided process. Google is doing its best to predict your needs regarding content, but it also listens to the signals you give them.
You can indicate that you want less or more of certain content. And you have control not only over the content that appears, but over the overall trajectory of your Google Discover’s work.
How Does Google Discover Work in Practice
Obviously, the phenomenon of Google Discover opens up new possibilities for all content creators.
This is a different kind of game than the usual Google search queries.
Of course, there are ways to leverage your “influence” on Google Discover regardless of what industry branch you are coming from.
1. Developing in Hobbies and Activities

Small research done by Search Engine Journal noticed that Google Discover’s main aim has been achieved. Most of Google Discover interests have been hobbies and activities, second to sports and entertainment.
This was the main aim of Google Discover – helping users on long journeys like advancing in a new hobby or activity.
Google Discover’s “queryless search” aims to put the user into focus more, abandoning instant answers and offering paths to developing skills and understanding.
2. Google Discover Policies
Just like the Google search engine, Google Discover has its own policies. In short, here are the most important ones:
- Avoid click-baiting and aim to have clear titles
- Aim to produce content that relates to current interests, tells a story well or provides unique insights.
- Provide clear dates, quotations, information about authors, publications, and such
- Use high-quality images in your content. Large images need to be at least 1200 px wide and enabled by the large image setting or by using AMP.
- Avoid using your brand’s logo as an image for your content.
3. Heavy Brand Representation

The research also finds that almost every interest submission contains a brand. The content offered up regarding users’ interest is always sought to come from a branded source. This can be interpreted in 2 ways:
- Google is aiming to offer relevant content coming from specialized brands related to a certain topic.
- Google is promoting existing brands, and encouraging brand creation.
Be it as it may, this is a very simple nod Google is giving – if you are a brand, Google Discover will give you more attention.
As you can see, these guidelines don’t contain anything that is not already included in Google’s Webmaster guidelines, though they do accentuate certain things.
Regardless, Google Discover advises content creators to keep track of their results using the Performance Report for Discover. The performance report keeps track of your content’s performance up to 16 months back.
Is Google Discover the New “news”
Well, seeing how the internet has been developing, and especially how Google has been aiming to spread its work to as many facets as it can, it wouldn’t be a surprise. And the research done by the Search Engine Journal indicates that truly 99% of clicks go to the news part of Google Discover.
They reported that news comprises almost half of the content (46%), but garners the huge majority of user attention. The other 1% of the clicks that did not go to the “news” is mostly blog posts.
Short Content Shelf-life
Continuing with the news analogy, it seems that most of the content presented on Google Discover is relevant only for a short while.
Most of the content analyzed by Search Engine Journal received traffic only for three to four days. The majority of it being gathered during the first and second day of its presence on Google Discover.
How to Succeed on Google Discover

The takeaway is that Google Discover really does ease some of the work for both users and content creators.
Users seem to respond well to Google Discover, and Google Discover seems to drive more traffic to the content it presents than the traditional query search does. This would mean that Google Discover has achieved its main goal of helping users make their queries into longer discovery-orientated journeys and giving content creators a bigger and more focused stage.
The most important information you have to take into consideration is that Google Discover is a mobile app, it is only available on mobile devices. So being mobile-friendly is a must if you aim to have any kind of attention on Google Discover.
To be sure you are doing this right, I suggest you check out Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability Report.
This of course draws with it most of the other suggestions for success on Google Discover. Apart from following the usual policies highlighted by Google Discover.
This means thinking ahead about the images you are going to use in your content, and keeping in mind that video is going to be important on an app like Google Discover. Updating your Youtube channel might also give you’re a boost on Google Discover.
A thing most content creators will see as beneficial to them is the fact that Google Discover is organized into topics. Most serious content creators are niche orientated and aim to specialize within a certain interest, and Google Discover tends to reward this kind of work.
The move from query-answering problem-solving to the longer development orientated approach of Google Discover will benefit all creators immeasurably.
Conclusion
Google Discover might seem like a “non-innovation”, something we have already seen in traces on all other platforms and is now made in Google’s own package. But, Google Discover is impacting the way users find and interact with content in a positive way, and content creators also seem to be benefiting from it.
It is also evidence of a wider push that information culture is taking, seeing the short-comings of instant answers when it comes to problem-solving.